2. How Videogrammetry Works
2.1 Basic Principles and Methods
Videogrammetry uses videos to make 3D models. It's like photogrammetry but with moving pictures. Here's how it works:
- Splits video into many images
- Looks at how images overlap
- Uses math to make 3D models
The quality of the 3D model depends on:
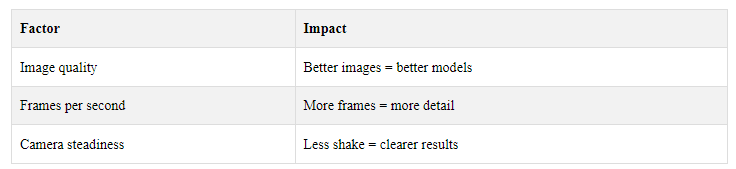
2.2 Videogrammetry vs. Photogrammetry
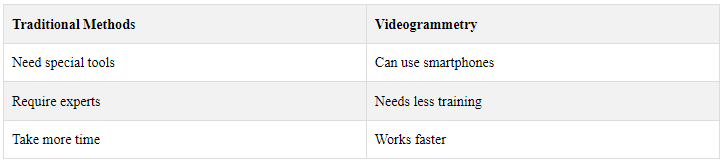
Both methods make 3D models from 2D images, but videogrammetry has some perks:
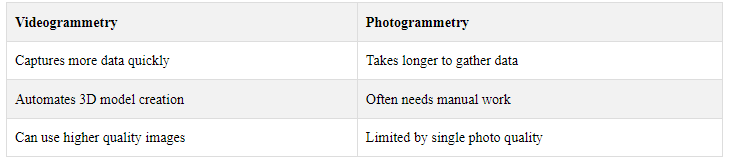
2.3 Tools and Equipment
To do videogrammetry, you need:
- Good video cameras
- GPS devices
- Gear to keep the camera steady
- Special computer programs
- You also need to know about:
How cameras work
- 3D modeling
- Computer vision
- These tools and skills help turn videos into useful 3D models.
3. Uses in Emergency Response
3.1 Improving Disaster Awareness
Videogrammetry helps in disaster awareness by making 3D models of affected areas. These models show:
- How much damage there is
- Where dangers might be
- Where help is needed most
- This helps emergency teams plan better and work more safely.
3.2 Quick Disaster Scene Analysis
3D models from videogrammetry let emergency teams check disaster areas fast. They can:
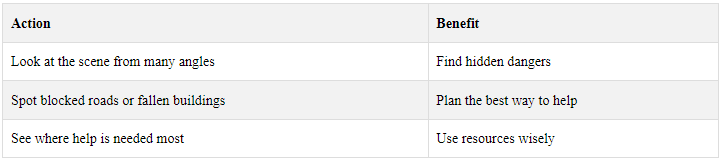
3.3 Helping Search and Rescue
Videogrammetry makes search and rescue work easier. The 3D models help teams:
Find places where people might be trapped
Check if buildings are safe to enter
Plan the safest routes for rescuers
This means they can find and help people faster and more safely.
3.4 After-Disaster Damage Review
After a disaster, videogrammetry helps check what's been damaged. It lets teams:
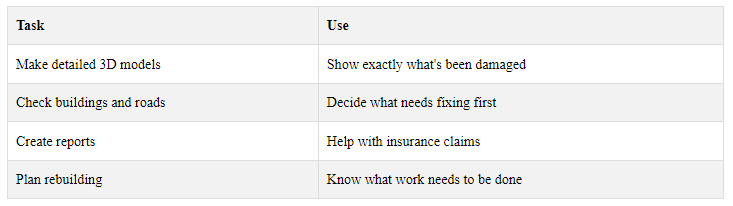
This makes recovery work faster and more organized.
4. Improving Infrastructure Management
4.1 Checking and Maintaining Assets
Videogrammetry helps manage infrastructure by making 3D models of assets like roads, bridges, and buildings. These models let managers:

4.2 Tracking Construction Progress
3D models from videogrammetry help track building projects. Managers can:
- See how work is going
- Spot delays or budget issues
- Share models with others to work better together
4.3 City Planning and Growth
City planners use videogrammetry to make 3D city models. This helps them:

4.4 Preserving Historical Sites
Videogrammetry helps keep old buildings and sites safe. People who look after these places can:
- Make a record of how the site looks now
- Plan how to fix things up
- Show 3D models to get help and money for projects
These 3D models help people understand and care for old places better.
5. Steps in Videogrammetry
5.1 Collecting Video Data
The first step is to record video of the object or area you want to model. You'll need:
- A good camera (can be a smartphone)
- GPS device (optional)
- Steady hands or a tripod
Tips for good video:
- High resolution
- Smooth movement
- Overlap between frames
5.2 Analyzing the Data
Next, special computer programs break down the video and study it. They:
- Split the video into separate images 2. Look at how the images fit together 3. Figure out 3D information from 2D pictures
The quality of your 3D model depends on how good your video is.
5.3 Creating 3D Models
Now the computer turns the video data into a 3D model:
- Makes a "point cloud "(lots of 3D dots) 2. Connects the dots to make a 3D shape 3. Adds color and texture
You can use these models to:
- Look at things from all angles
- Take measurements
- Run simulations
5.4 Working with Other Mapping Tools
Lastly, you can use your 3D model with other map tools:
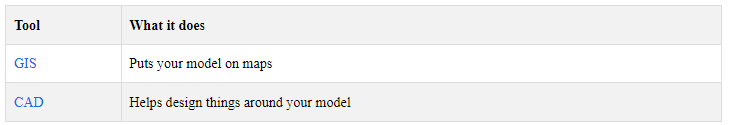
Using these tools together helps you:
- See how your model fits in the real world
- Plan projects better
- Make smarter choices about land and buildings
6. Benefits of Videogrammetry
6.1 Fast Data Collection
Videogrammetry helps collect data quickly. This is very useful in emergencies when time matters. Emergency teams can:
- Take videos of the area fast
- Make 3D models from these videos
- Use the models to plan their work
6.2 Lower Costs
Videogrammetry can save money. Here's how:
This means less money spent on equipment and workers.
6.3 Better 3D Models
Videogrammetry makes good 3D models because:
- It takes many pictures from different angles
- These pictures join to make detailed models
- The models show things clearly
This helps in building projects and checking structures.
6.4 Works in Many Places
Videogrammetry is useful in different areas:

It's easy to use in many places because you can carry the tools with you.
7. Problems and Limits
7.1 Technical Issues and Equipment Needs
Videogrammetry has some problems:
Needs good cameras and software
- Can be expensive
- Hard to use in bad weather or poor light
- Tricky to film in messy areas like disaster zones
7.2 Managing Large Data Sets
Videogrammetry makes a lot of data. This can cause issues:

7.3 Privacy Concerns
Taking videos for 3D models can cause privacy issues:
- People might be filmed without knowing
- Some worry about too much watching
- Need clear rules about how to use the videos
7.4 Legal Rules
Using videogrammetry must follow laws:

It's important to know these rules to avoid problems.
8. Future of Videogrammetry
8.1 Using AI and Machine Learning
AI and Machine Learning will make videogrammetry better:
- Faster 3D modeling
- Better object tracking
- Less manual work
AI could help process data quicker, saving time and effort.
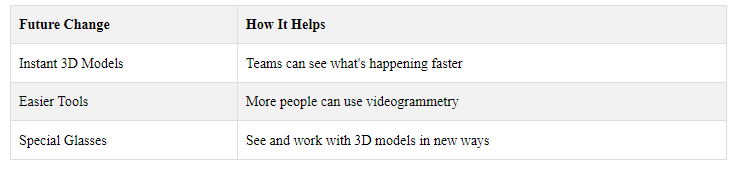
8.2 Instant 3D Model Creation
Soon, we might be able to make 3D models right away. This would help:
- Emergency teams act faster
- Managers make quick choices
- People understand situations better
Quick 3D models mean less waiting and faster action.
8.3 Smaller, Easier-to-Use Tools
New tools for videogrammetry will be:
- Smaller
- Easier to use
- More portable
This means more people can use videogrammetry, even in places with few resources.
8.4 Combining with AR and VR
Mixing videogrammetry with AR and VR could:
- Make training more real
- Help people see plans better
- Let teams practice for emergencies
This mix of tech could make work safer and more effective.

These changes will make videogrammetry more useful for emergency response, building projects, and other work. As the tech gets better, more people will be able to use it to understand and work with the world around them.
9. Tips for Using Videogrammetry
9.1 Training Staff
To help staff use videogrammetry well:
- Teach the basics first
- Let them practice with the tools
- Show how it's used in real jobs
- Keep learning about new things in videogrammetry
9.2 Choosing the Right Tools
Pick the best tools for your work:

9.3 Setting Up Good Work Processes
Make sure your team works well:
- Write down how to do the work
- Tell everyone what their job is
- Use lists to check all steps are done
- Keep making your work better
####9.4 Keeping Data Safe and Ethical
Take care of the information you collect:

These tips will help you use videogrammetry better in your work.
10. Real-World Examples
10.1 Emergency Response Examples
Videogrammetry helps in emergencies by making 3D models of damaged areas. This lets teams:
- See what's broken
- Find dangers
- Plan how to help
For example, after a flood, teams can use 3D models to see which areas need help first.
10.2 Infrastructure Project Examples
Building teams use videogrammetry to:
- Check how work is going
- Spot problems early
- Make sure everything is built right
For instance, they can make 3D models of a building site to see if work is on track.
10.3 Key Lessons from These Examples
These examples show how videogrammetry helps in emergencies and building work. Here's what we learned:
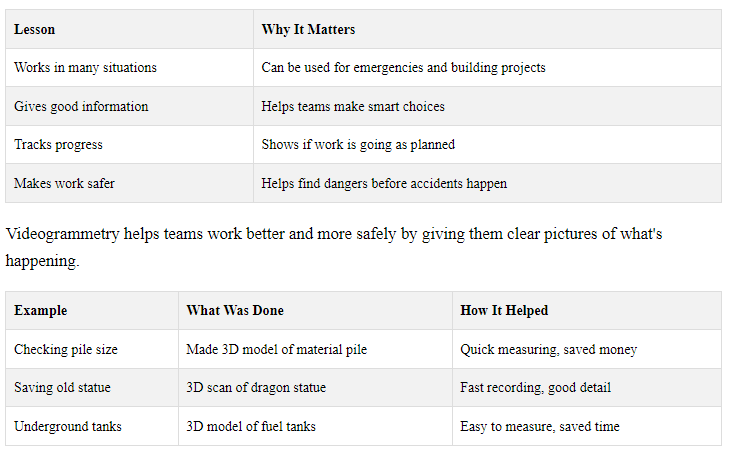
These examples show how videogrammetry can help in different kinds of work, from building sites to saving old things.
11. Conclusion
11.1 How Videogrammetry Helps
Videogrammetry has changed how we handle emergencies and manage buildings. It makes 3D models that help teams:
- Make smart choices
- Act fast in emergencies
- Do building work better
Here's what makes videogrammetry good:

11.2 What's Coming Next for Videogrammetry
Videogrammetry keeps getting better. Soon, it might:
- Make 3D models right away
- Use smaller, easier tools
- Work with special glasses to show 3D things
As videogrammetry gets better, it will help even more with emergencies and building work.



















